Unlocking the Secrets of User-Friendly Design: Exploring Jakob Nielsen’s 10 Usability Heuristics
Design

Shaik Moosa
April 3, 2024 | 4 min
Share to

Heuristics form the cornerstone of user experience (UX) design, providing a framework to create intuitive and effective digital products. Below, we delve into each of these heuristics, discussing how they contribute to a seamless user interaction with technology.
Visibility of System Status
The system should always keep users informed about what is going on, through appropriate feedback within a reasonable time.
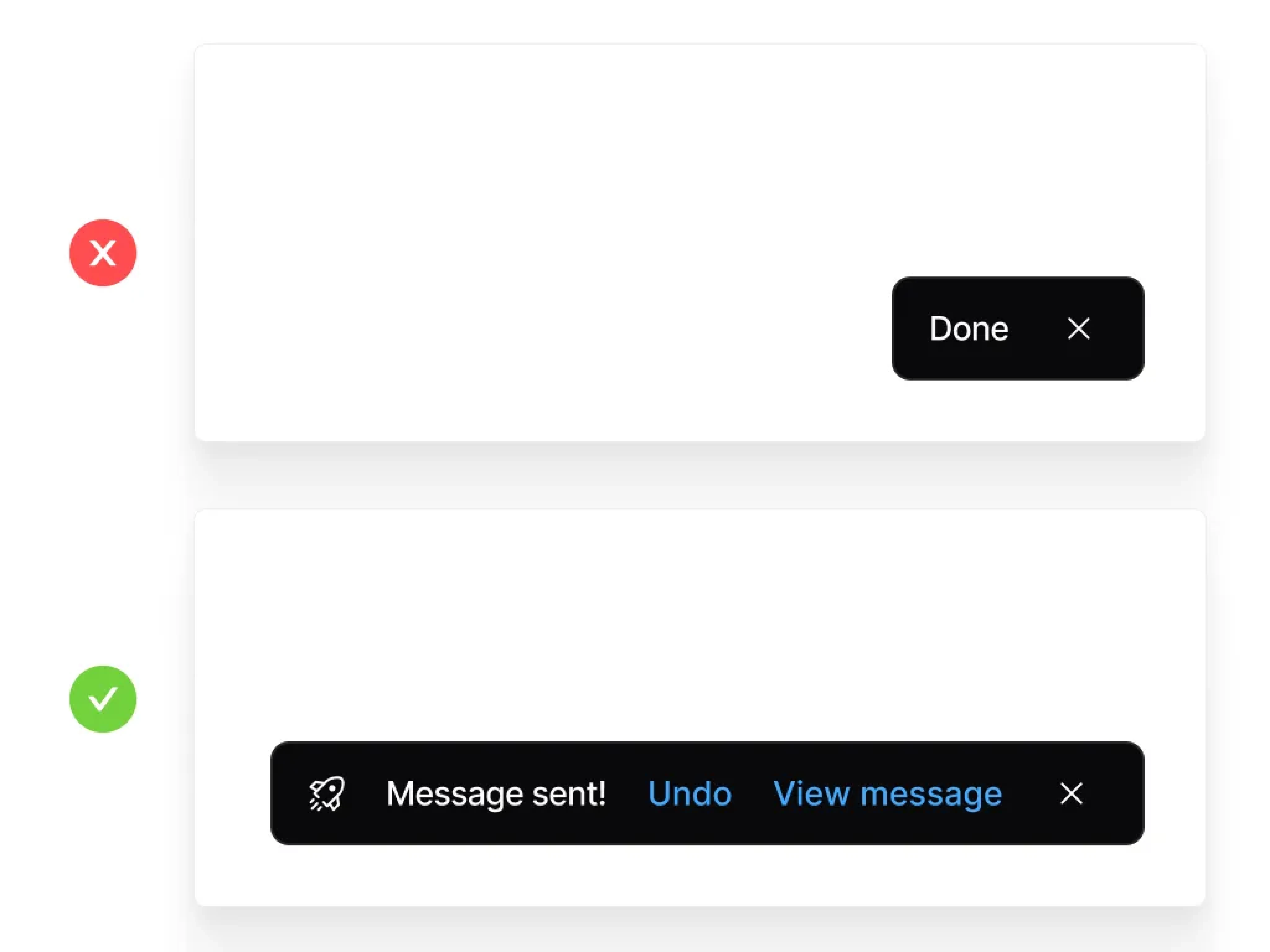
Key Elements:
- Progress indicators for long operations
- Clear messages about the current state of the system
- Real-time updates reflecting system changes
There are 4 possible feedback types a good system should provide:
- What has just happened
- Where am I?
- What is happening?
- What will happen next?
Match Between the System and the Real World
The system should speak the user’s language, with words, phrases, and concepts familiar to the user, rather than system-oriented terms.
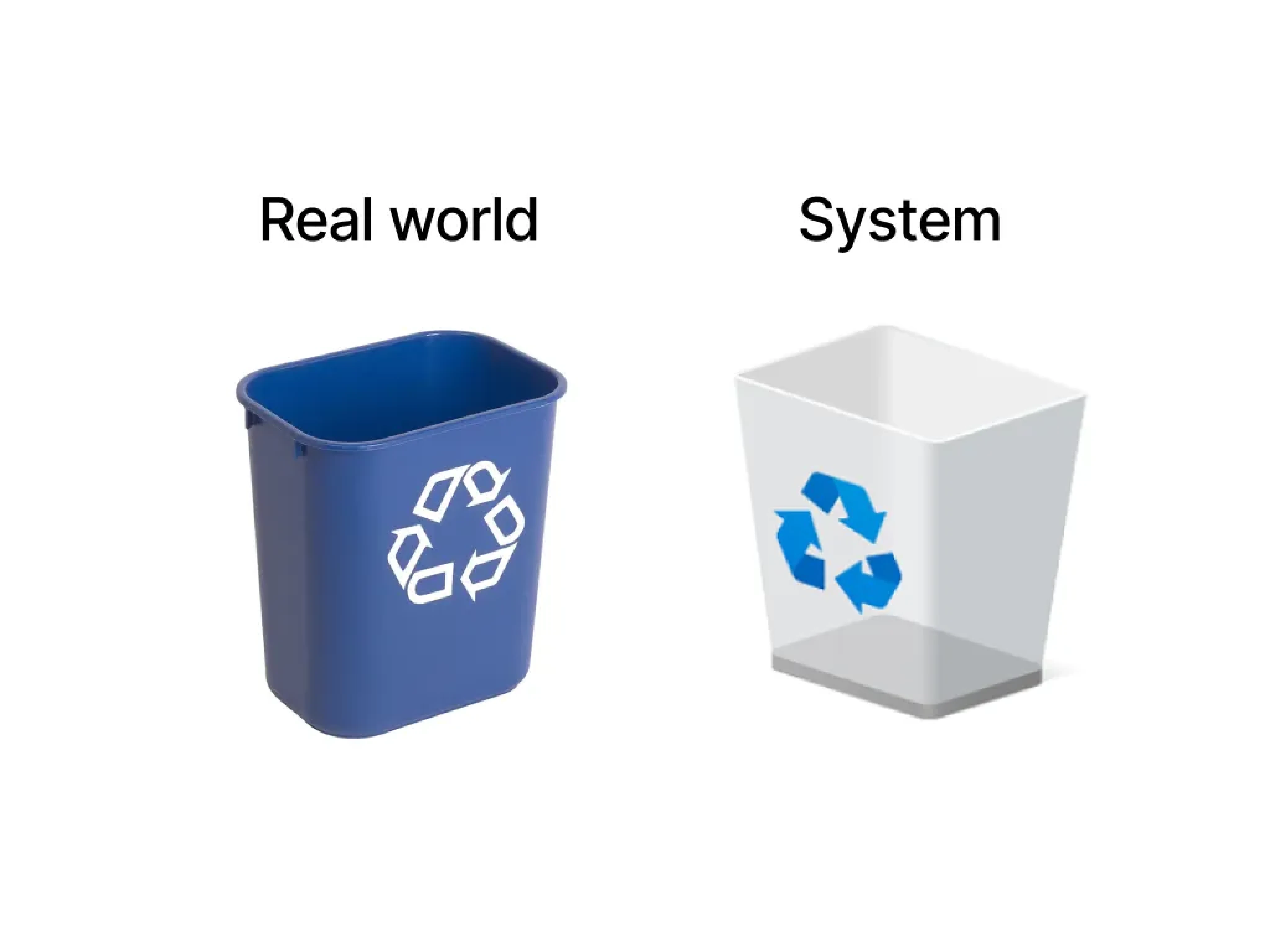
Key Elements:
Use of real-world metaphors and conventions
Clear and natural dialogue
Information presented in a logical order
User Control and Freedom
Users often perform actions by mistake. They need a clearly marked “emergency exit” to leave the unwanted state without having to go through an extended dialogue.
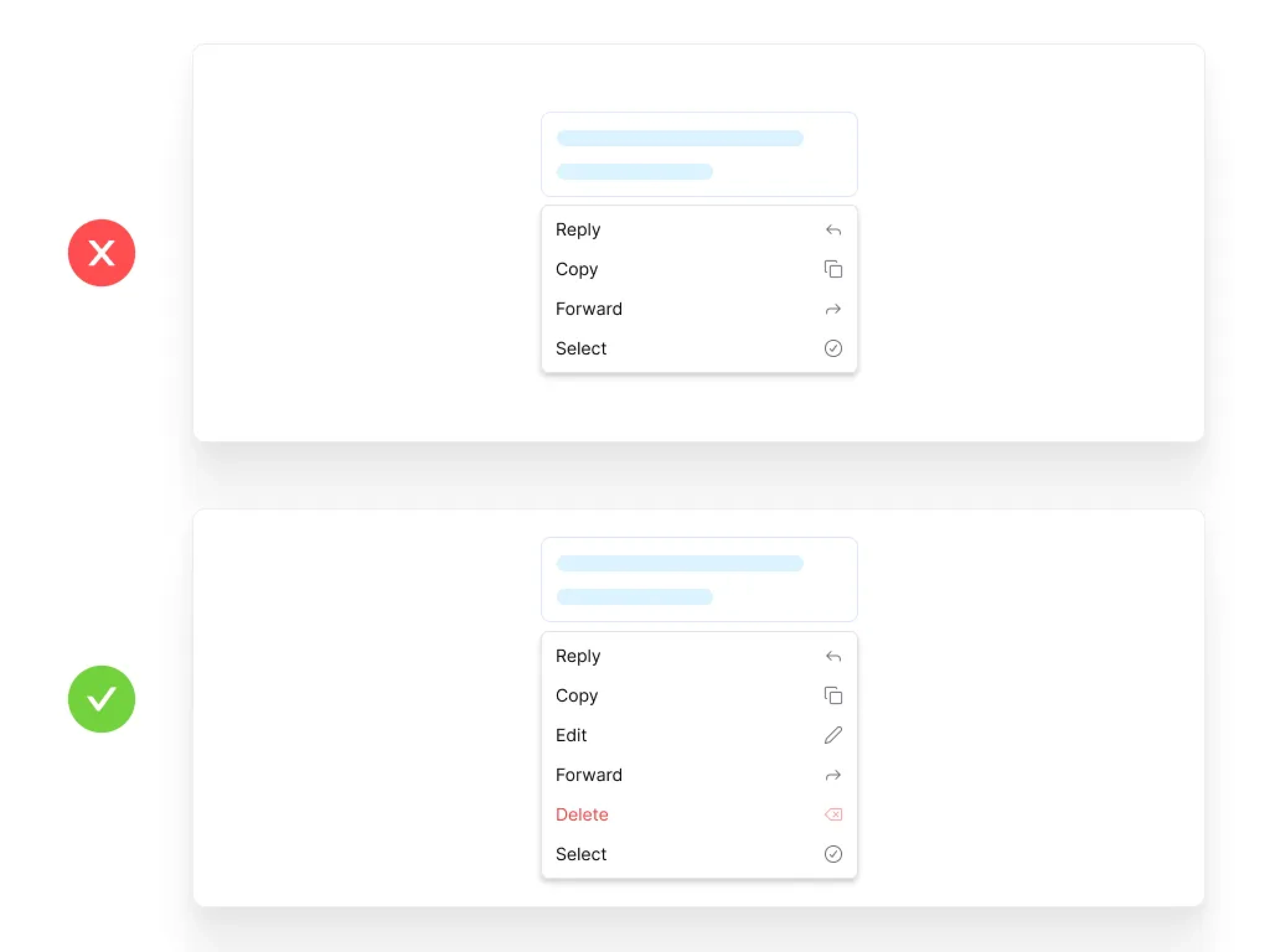
Key Elements:
Undo and redo functions
Easy navigation back and forth
Freedom to explore without getting trapped
Consistency and Standards
Users should not have to wonder whether different words, situations, or actions mean the same thing. Follow platform and industry conventions.
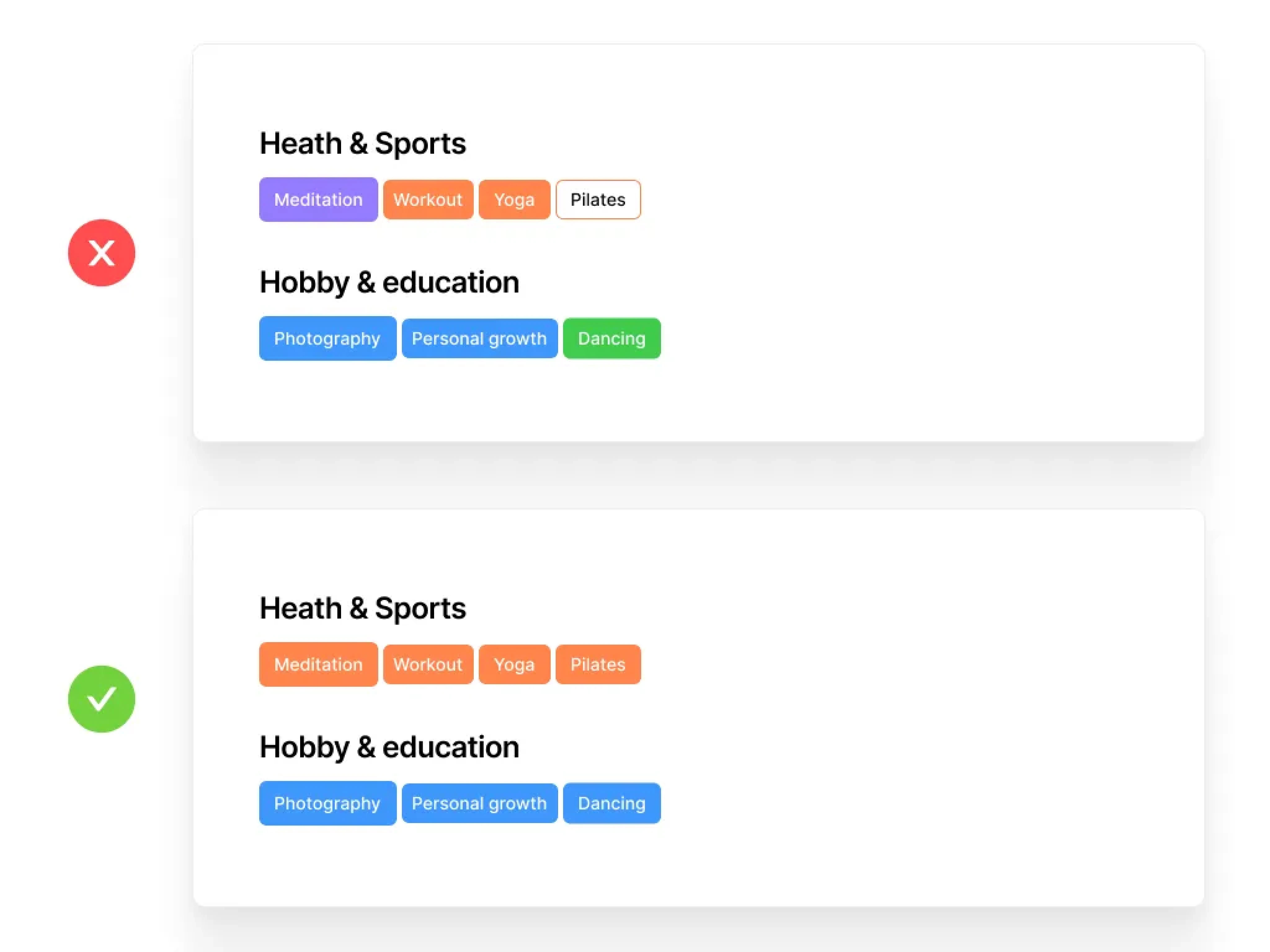
Key Elements:
Consistent terminology
Adherence to platform guidelines
Predictable interactions
Error Prevention
Even better than good error messages is a careful design that prevents a problem from occurring in the first place.
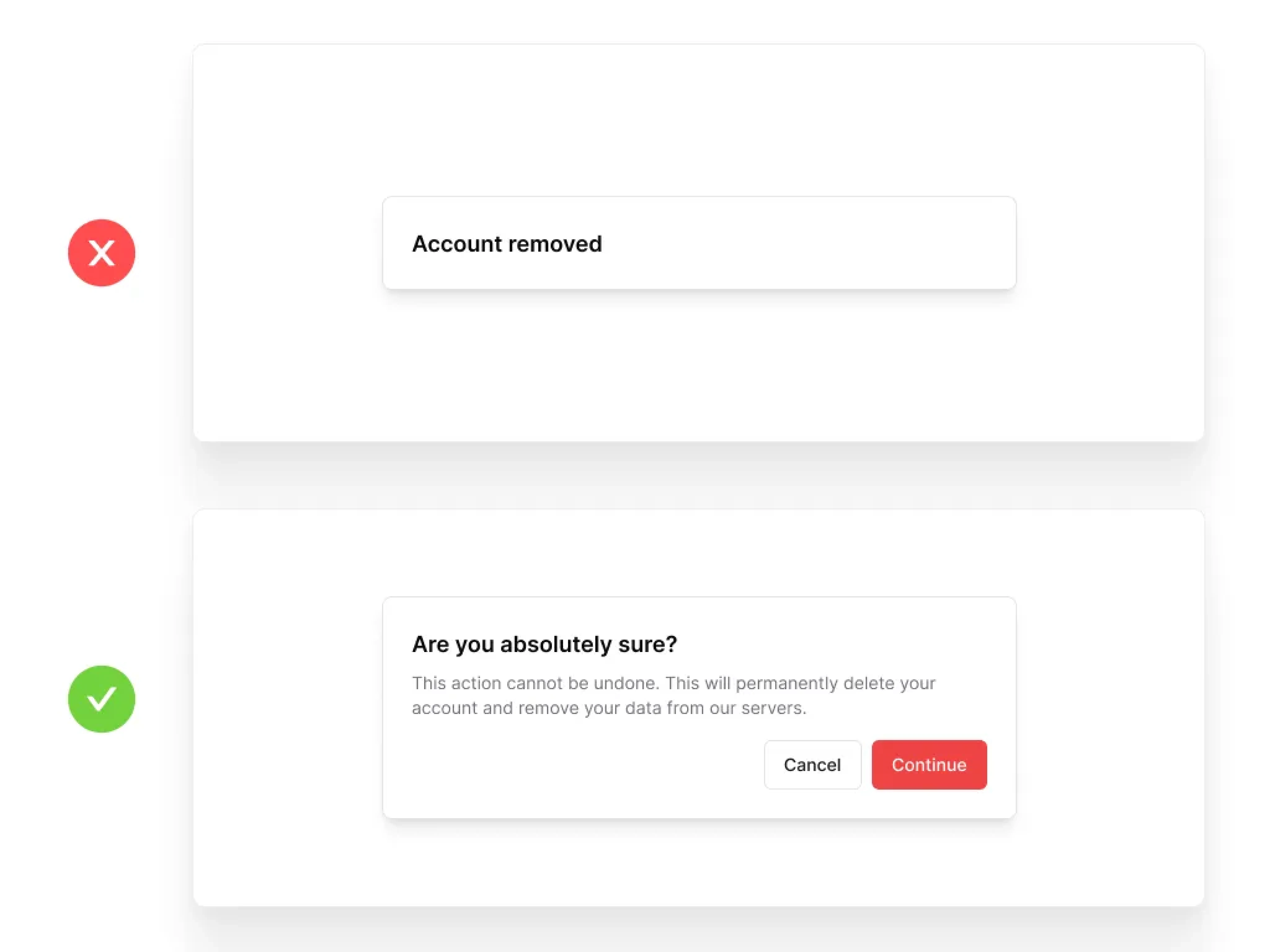
Key Elements:
Confirmation dialogues for critical actions
Helpful constraints to prevent errors
Context-sensitive help
Recognition Rather Than Recall
Minimize the user’s memory load by making objects, actions, and options visible. The user should not have to remember information from one part of the dialogue to another.
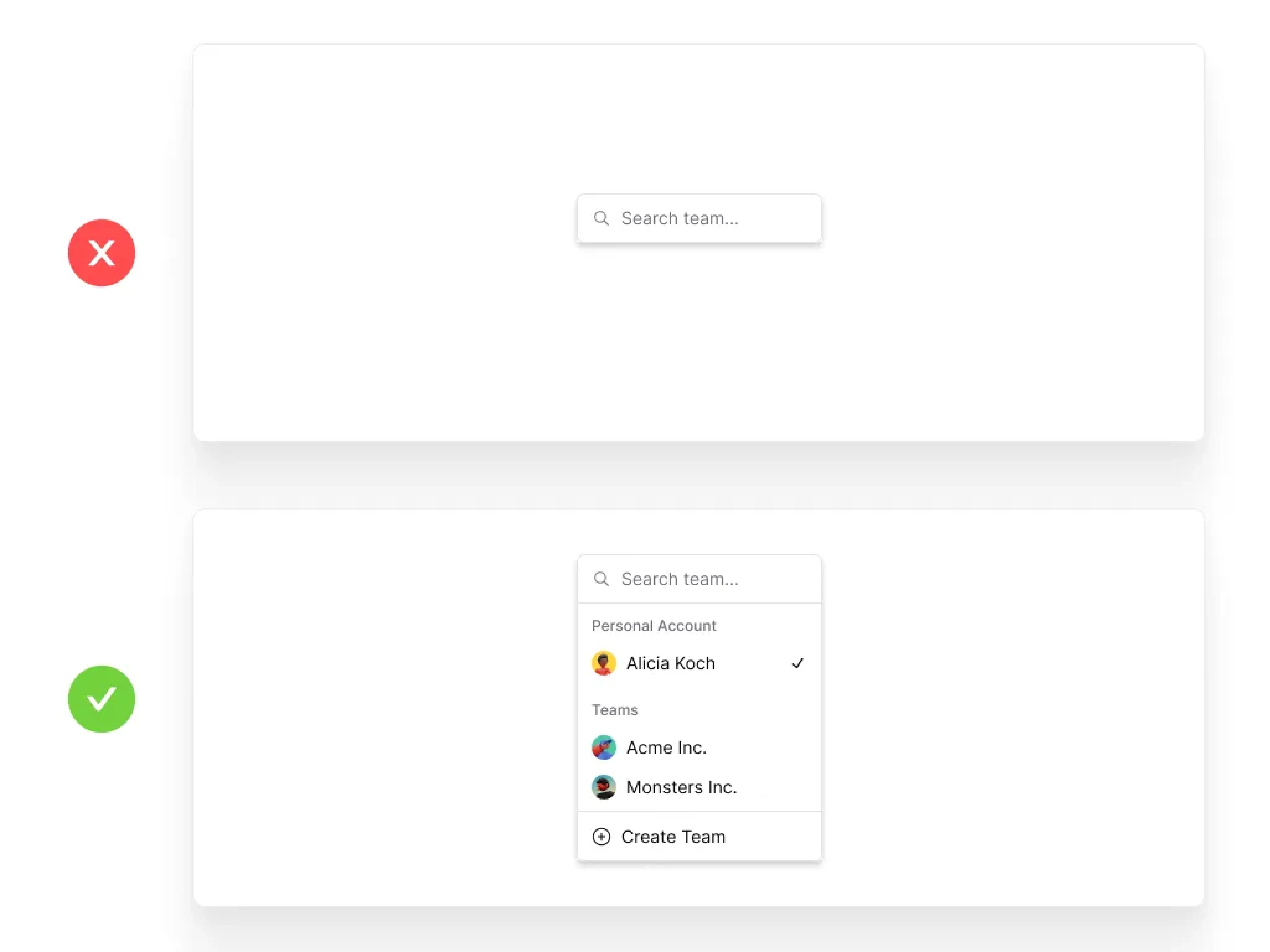
Key Elements:
Visible instructions for use of the system
Easily retrievable options and information
Elimination of unnecessary complexity
Flexibility and Efficiency of Use
Shortcuts — hidden from novice users — may speed up the interaction for the expert user such that the system can cater to both inexperienced and experienced users.
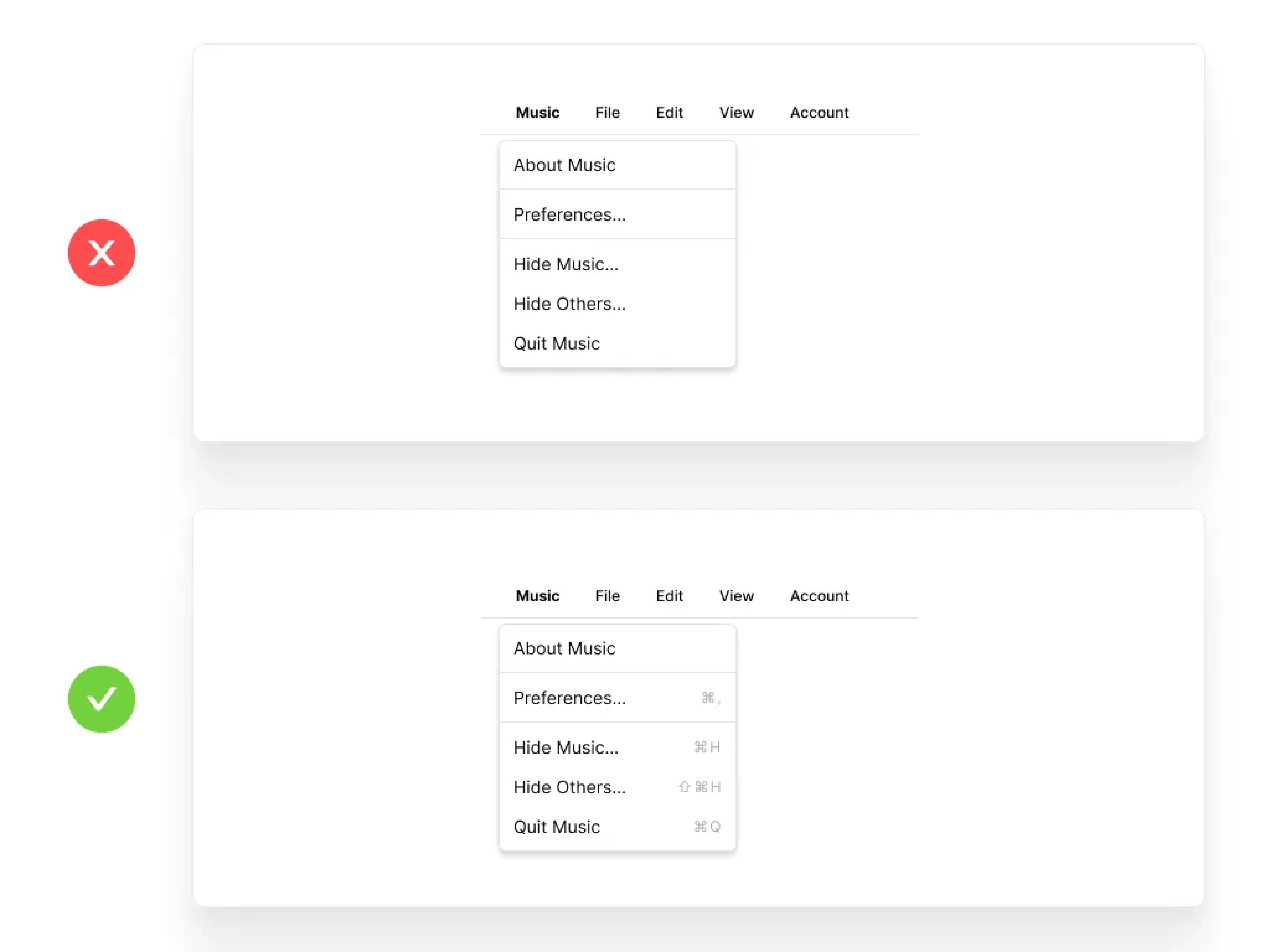
Key Elements:
Customizable features
Accelerators for frequent actions
Personalized user experiences
Aesthetic and Minimalist Design
Dialogues should not contain information that is irrelevant or rarely needed. Every extra unit of information in a dialogue competes with the relevant units of information and diminishes their relative visibility.
Key Elements:
Clean and focused design
Elimination of non-essential elements
Emphasis on key information
Help Users Recognize and Recover from Errors
Error messages should be expressed in plain language (no codes), precisely indicate the problem, and constructively suggest a solution.
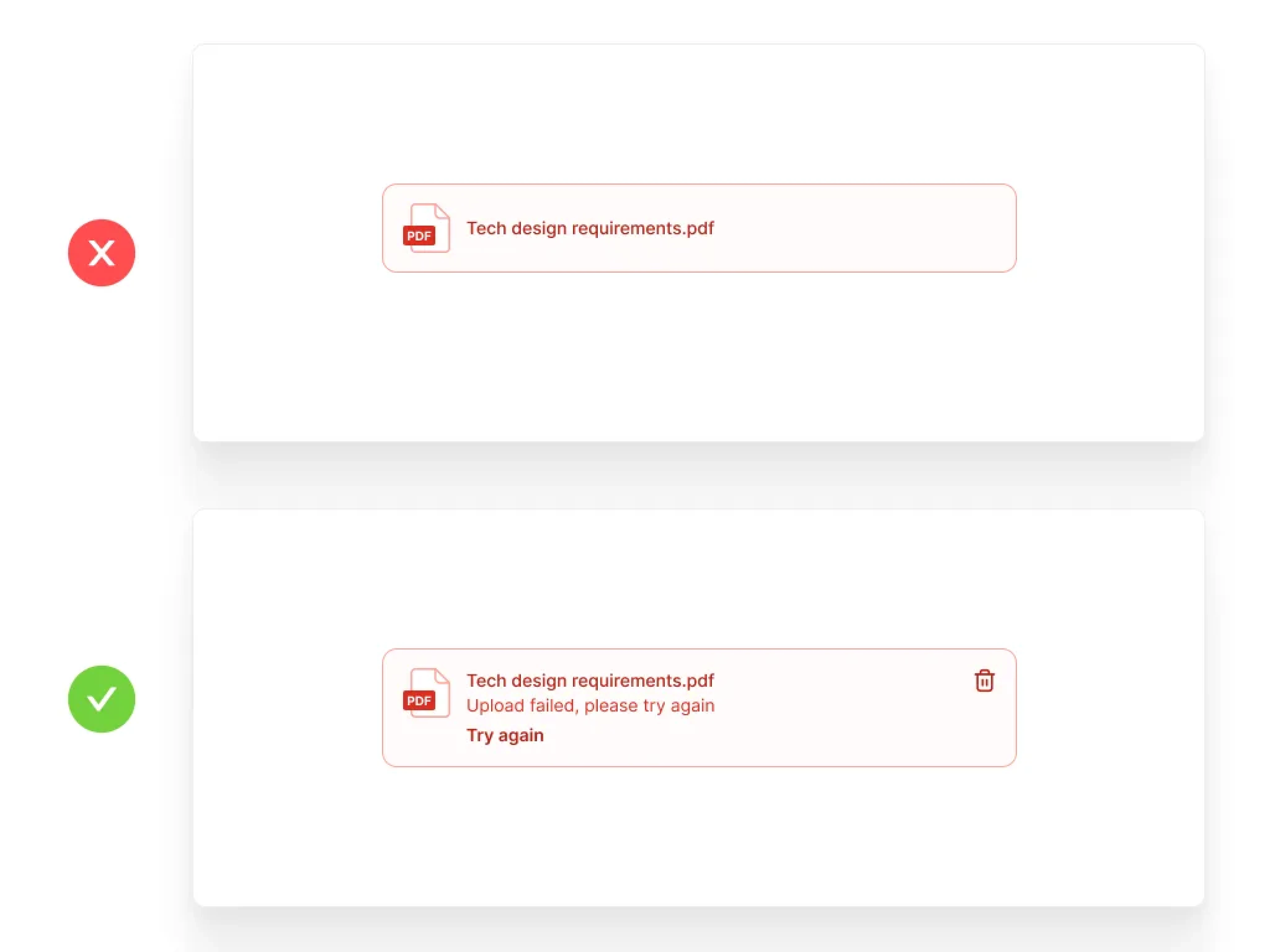
Key Elements:
Clear error messaging
Guidance on error resolution
Supportive tone in communications
Help and Documentation
It may be necessary to provide documentation to help users understand how to complete their tasks.
Key Elements:
Easy-to-search help content
Task-focused instructions
List of concrete steps to solve problems
The Heuristic Evaluation Process
Conducting a heuristic evaluation involves a systematic inspection of a user interface. Expert evaluators examine the interface and judge its compliance with the above usability principles.
Steps for Conducting Heuristic Evaluation:
- Familiarize evaluators with the system and heuristics
- Individually assess the interface against the 10 heuristics
- Compile and discuss findings
- Prioritize issues and provide actionable recommendations
Benefits of Heuristic Evaluation:
- Quick and relatively inexpensive
- Identifies usability problems effectively
- Can be conducted with or without user involvement
By embracing and implementing Jakob Nielsen’s 10 Usability Heuristics, designers and developers can craft user-centric interfaces that foster efficiency, clarity, and satisfaction. These principles are as relevant today as they were at their inception, continuing to guide the evolution of digital product design.
Get started today at ApptDev
Sources
- Nielsen, J. (n.d.). 10 Usability Heuristics for User Interface Design. Nielsen Norman Group. Retrieved from nngroup.com
- Simplified: Jakob Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics — Bootcamp. (n.d.). UX Collective. Retrieved from uxdesign.cc
- Nielsen’s 10 Usability Heuristics — Heurio. (n.d.). Heurio. Retrieved from heurio.co
- 10 Usability Heuristics by Jakob Nielsen Lesson — Uxcel. (n.d.). Uxcel. Retrieved from uxcel.com
- Nielsen’s Heuristics: 10 Usability Principles To Improve UI Design. (n.d.). Aela School. Retrieved from aelaschool.com
FAQs
Related Blogs

Can you really build an app with no-code?
In a world where digital transformation is no longer optional, the ability to create custom applications quickly has become a competitive advantage.
Read More
How to create an AI app without coding?
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, artificial intelligence has transformed from an exclusive domain of specialized developers to an accessible tool for businesses and individuals alike.
Read More
How to Build a Simple App to Track Your Inventory—No Coding Needed
Here’s a concise guide to building a custom inventory-tracking app on ApptDev—no coding required. You’ll learn why inventory management matters, how ApptDev’s visual tools streamline every step, and key insights to maximize efficiency. By following our six-step walkthrough, you’ll go from blank canvas to deployed app in under an hour, complete with automated reorder alerts and mobile-ready interfaces.
Read More